Anesthesia is an essential technique that is used on a daily basis both in medicine and in the specific case that concerns us, that is, in the field of dentistry. Dental anesthesia allows us to carry out procedures that we would otherwise not be able to perform.
Or that, in the case of performing them, would cause pain that would be almost impossible for the patient to bear. There are different types of anesthesia in dentistry and the choice of one method or another depends on the type of dental treatment the person is undergoing.
What is oral anesthesia?
By dental anesthesia we mean that which aims to eliminate the sensitivity of a specific area of our body: the mouth. In this way, dentists can perform any treatment that the patient needs in a painless and comfortable way. While the anesthesia lasts, the person will not feel anything in the area and, depending on the type of anesthesia, he or she will remain conscious or not.
We will now go into more detail on this subject, explaining the types of dental anesthesia that exist and in which treatments they are applied.
What anesthesia and sedation techniques are there?
Within dental techniques there is a wide variety of forms of sedation.
Even so, not all dental clinics can offer them to their patients, either because of the equipment they require or because of the specialization needed by the professionals. Therefore, if you are interested in a particular anesthesia, we recommend that you ask beforehand if it is available at the clinic you are going to visit.
At DrAW Dental Clinic we are committed to investing in new techniques that make it easier for the patient to go to the dentist, which is why we use all types of dental anesthesia.
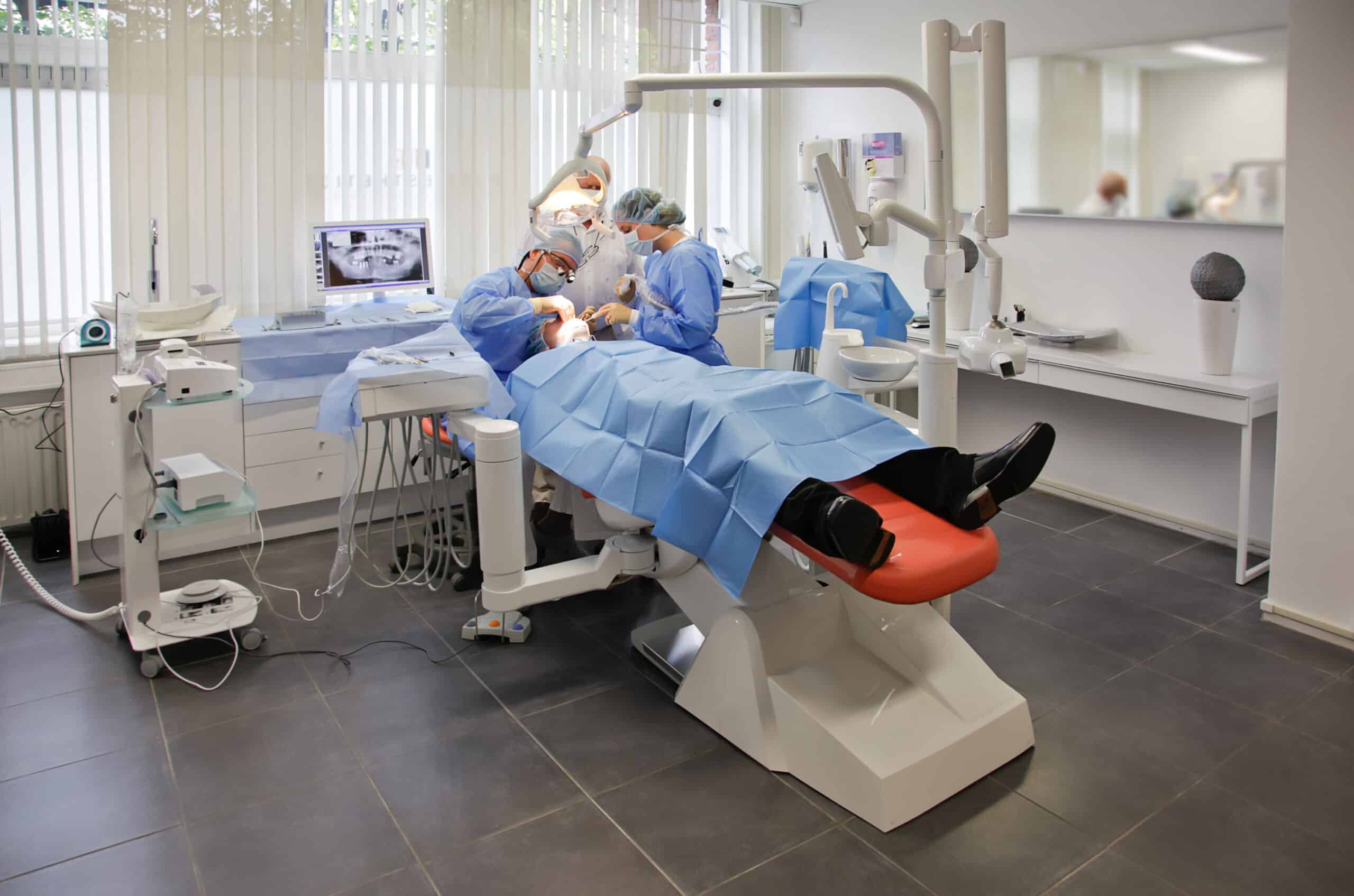
There are different types of anesthesia
Enlarge image
DENTAL TREATMENT
Local anesthesia
Local anesthesia in dentistry is the most commonly used technique to eliminate sensitivity in the mouth. This is because it can be applied in any oral treatment that generates pain or discomfort to the patient. Examples of such interventions would be dental fillings, root canals, implants or extractions.
However, although it is not usual, the dentist can also apply local anesthesia in dental hygiene. This is done in cases in which the patient has a lot of plaque and subgingival dental tartar, and its removal is excessively annoying. The ideal is not to have to reach this point of tartar accumulation, so we always recommend our patients to visit the clinic every year for a professional cleaning.
Anesthetic spray, cream or gel
Anesthetic gels, creams or sprays are used to numb the area where an operation is to be performed. Therefore, they are a type of topical dental anesthesia and are used to avoid the pain caused by the “prick” of the needle with which the anesthetic is applied.
As they have a very mild and limited effect, these products are not used on their own in the treatments mentioned in the previous point: fillings, root canals, implants, veneers or extractions. In other words, they are only used to apply local anesthesia afterwards.
Find out about the techniques
Although the dentist can explain the types of dental anesthesia and sedation, we recommend that you know the difference between them.
Light sedation with nitrous oxide
Mild sedation is a technique that consists of the application of nitrous oxide and oxygen by means of a mask. Therefore, since it is inhaled -rather than injected- it avoids using a needle and pricking the patient. The mixture of these gases allows the person to remain in a state of consciousness for the duration of the treatment.
Fundamentally, it is used in the specialty of periodontics, specifically in periodontal maintenance. The reason why it is used in this type of procedure is because there is more discomfort than with a simple professional cleaning. However, the pain is more bearable than that caused by other treatments, so it is not necessary to apply local anesthesia.
COME TO YOUR FIRST APPOINTMENT FOR FREE
Conscious Sedation
Of all the techniques we are discussing, conscious sedation is the least frequently used in dental clinics. Although in our dental clinic we have this technique, the truth is that it is not at all common. This is because it is necessary to have a cabinet equipped for it, as well as an anesthesiologist.
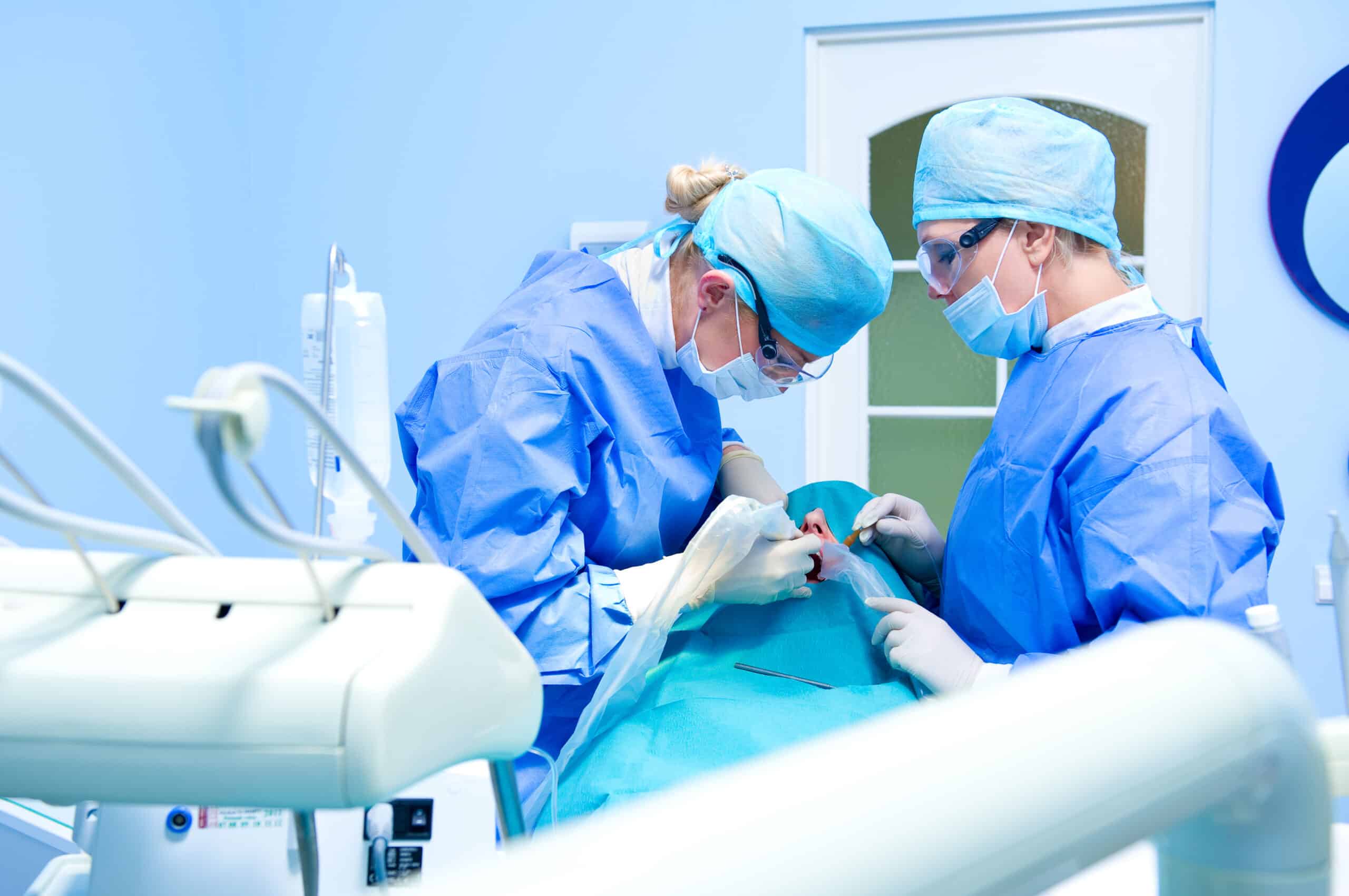
Advanced sedation technique
Enlarge image
CONSCIOUS SEDATION
In our clinic, we have the experience of Arturo Sánchez Feria, Doctor in Medicine and Surgery and specialist in Anesthesiology and Resuscitation. Conscious sedation can be applied in any dental treatment, but it is most commonly used in dental implant surgeries.
It should be noted that it is not an anesthetic technique as such, but is performed when patients feel fear or anxiety before the surgical procedure. Therefore, conscious sedation is always used together with local anesthesia.
In fact, in people who are going to undergo implant surgery and do not feel any anxiety, only local anesthesia is used.
General anesthesia
Finally, general anesthesia is an induced coma that does not take place in the dentist’s office, but is used in a hospital environment. However, it can be used for certain oral surgical procedures, such as orthognathic surgery, dental implants or wisdom tooth extraction.
As a general rule, local dental anesthesia is used for all treatments except orthodontics and whitening.
Types of local dental anesthesia
Within the types of local anesthesia that we have previously explained, we distinguish between three:
Troncular
This is the one commonly used to numb the lower -arched- part of the mouth. To anesthetize the area, it is applied near the lower dental nerve and manages to numb half of the arch, the tongue and the lip.
Infiltrative
Contrary to the truncal anesthesia, the infiltrative anesthesia is usually placed in the upper arch, but also in the lower arch when it is necessary to numb a more specific area. In children, this type of anesthesia can also be placed in the lower arch.
Intraligamentary
Intraligamentary anesthesia is not administered in the gum as the previous ones, but between the dental bone and the ligament. It is applied after the truncal anesthesia when there are very localized and extensive infections, such as endodontics. Thus, it is indicated in dental treatments of longer duration.
In which treatments is dental anesthesia applied?
As we have already seen in the previous section, the concept of “dental anesthesia” can include different sedation techniques. Therefore, depending on what we understand by oral anesthesia, we can say that it is convenient to use it in some treatments or others.
In certain cases, it is even possible to combine several types, as is the case with conscious sedation or dental anesthetic spray. In addition to this, remember that dental anesthesia can be applied in any treatment that generates pain, discomfort or discomfort to the patient.
Applying anesthesia
Enlarge image
DENTAL ANESTHESIA
To whom can oral anesthesia be applied?
We have talked throughout the article about the need to administer anesthesia in case the treatment is going to generate pain. However, the condition of each patient must be taken into account before applying anesthetic products. In the case of conscious sedation, it is essential to perform some tests on the patient requesting it.
Thus, the professional will perform a blood coagulation test, an electrocardiogram and a series of questions about the patient’s general health. In this way, we will obtain the necessary information to ensure that the entire treatment runs smoothly. On the other hand, this type of technique can also be used on children.
When is no anesthetic technique used?
Once we have made reference to the treatments in which anesthesia is used, we can say that there are others in which it is not necessary to do so. For example, anesthesia is not used in orthodontic or dental whitening treatments. As it could not be otherwise, this is because the possible discomfort generated is minimal and perfectly bearable for the person.
How long does the dentist’s anesthesia last?
Local dental anesthesia usually disappears completely between 1 and 3 hours. During this time, the patient will recover mobility and sensitivity in the area asleep.
On the other hand, the effect of nitrous oxide begins to reverse as soon as the patient stops breathing it through the mask, i.e., once the intervention has been completed and the dentist cuts off the gas supply. After approximately 20 minutes of normal breathing, the effects disappear. Even so, we recommend that the patient does not drive for the next 4 hours.
Finally, conscious sedation lasts the longest, as it is administered intravenously. Generally, the effect disappears completely after about 6 hours, but this time may vary according to each patient. It is quite normal to feel a sensation of numbness or even to experience amnesia in the hours that follow.
After undergoing an operation under this sedation, we advise the patient to leave the clinic accompanied at all times by another person and should not drive, consume alcohol or make relevant decisions.
Having made this distinction between the different anesthetic and sedation methods, we hope we have helped you to distinguish between them. In any case, you can ask us all your questions by contacting us or attending a free initial consultation.
You will be interested in ” Nitrous oxide sedation: lose your fear of the dentist!